Shell and tube condenser are used in exhaust gas treatment to condense exhaust gas or dirty vapors into liquid. Our condensers are divided into two types: water-cooled condensers and air-cooled condensers.
Cooling medium: Water-cooled Shell and tube condenser use water as the cooling medium, absorbing heat through the circulating flow of water and condensing gas or vapor into liquid. Air-cooled condensers use air as the cooling medium, and condensation is realized through convection and heat transfer of air.
Cooling method: Water-cooled Shell and tube condenser takes away the heat through the circulating flow of water to realize condensation. Cooling towers or chillers are usually used to lower the temperature of the water, which is then recycled. Air-cooled condensers, on the other hand, utilize air convection and heat transfer to cool, and increase air flow through a fan to improve the cooling effect.
Application environment: air-cooled condensers are suitable for places with low ambient temperature and good air flow, such as outdoor or well-ventilated areas. Water-cooled condensers are suitable for places with high ambient temperatures or where large amounts of heat need to be discharged, such as high-temperature industrial environments.
The choice of air-cooled or water-cooled Shell and tube condenser requires a combination of factors such as application environment, efficiency requirements, maintenance costs and economic costs to find the most suitable solution.
Simple and convenient: air condenser does not need additional cooling medium, just use the convection and heat transfer of air to realize condensation, installation and maintenance is relatively simple.
Wide range of application: Since it does not rely on a specific cooling medium, air condenser is suitable for a variety of environments and places, including home air conditioning, automotive cooling systems, etc.
Energy saving and environmental protection: compared with water condenser, air condenser does not need additional water circulation and treatment, which reduces the consumption of water resources and is more energy saving and environmental protection.
Efficient Cooling: Water condensers typically have high cooling efficiencies and are able to remove heat more efficiently, making them suitable for applications with high cooling requirements.
Suitable for large-scale systems: Water condensers are suitable for large-scale industrial equipment or systems because of the high heat capacity and heat transfer efficiency of water.
Good stability: water condenser can provide relatively stable cooling effect, not affected by the ambient temperature and air flow, suitable for some applications with high stability requirements.
The right type of condenser needs to be selected based on specific application requirements, environmental conditions and economic costs to maximize the benefits and meet the needs.
Model:
| model | Heat exchange area | power | Material | Shipping dimensions | Shipping Weight |
| CZSL-1000-70 | 70㎡ | Heat sink stainless steel, cylinder carbon steel | 3722*1356*1158 mm | 2150 kg | |
| CZSL-1000-90 | 90㎡ | Heat sink stainless steel, cylinder carbon steel | 4722*1466*1202mm | 2250 kg | |
| CZFL-8000-252 | 2020㎡ | 2.2KW*6 | Stainless steel | 8530*1860*1475mm | 3000kg |
| CZFL-9000-400 | 3000㎡ | 5.5KW*5 | Stainless steel | 8580*2100*1350mm | 3600kg |
The right type of condenser needs to be selected based on specific application requirements, environmental conditions and economic costs to maximize the benefits and meet the needs.
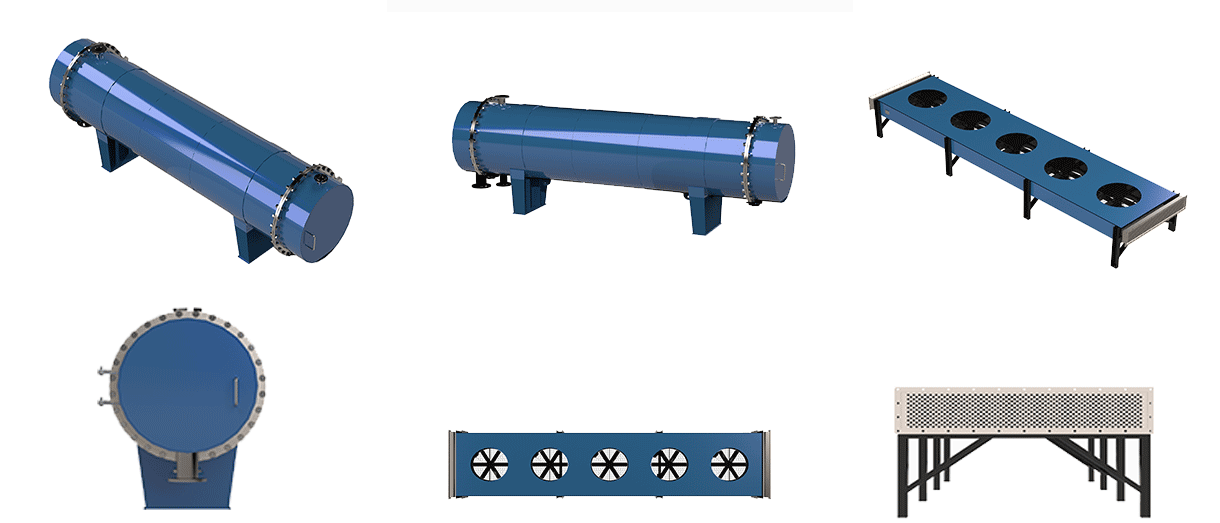
The choice of air-cooled or water-cooled condenser requires a combination of factors such as application environment, efficiency requirements, maintenance costs and economic costs to find the most suitable solution.